The electronics industry is experiencing transformative changes driven by advancements in technology and innovative designs, particularly in the domain of PCB fabrication and assembly. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global printed circuit board market is expected to reach USD 84.45 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 3.6%. This growth is propelled by the increasing demand for miniaturized electronic components and the integration of IoT devices across various sectors, enhancing connectivity and efficiency. As manufacturers strive for improved performance and reduced lead times, exploring novel techniques in PCB fabrication and assembly becomes essential. Embracing automation, additive manufacturing, and advanced materials will not only streamline production processes but also enable the creation of more complex and reliable electronic products. This article delves into these evolving techniques and their potential impact on the future landscape of innovative electronics.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) fabrication and assembly techniques form the backbone of modern electronic devices. At its core, PCB fabrication involves several key processes, including substrate preparation, layer stacking, and circuit patterning. The choice of materials—such as FR4, polyimide, or aluminum—greatly affects the performance and durability of the final product. Techniques like etching and drilling are crucial as they define the circuitry and connectivity that underpin the electronic design. Understanding these foundational steps can help engineers optimize designs for specific applications, ensuring efficiency and functionality.
Assembly techniques further enhance PCB performance, focusing on how electronic components are attached to the circuit board. Common methods include through-hole and surface mount technology (SMT), each with distinct advantages. SMT, for instance, allows for a higher component density and reduces the overall size of the devices, which is vital in the era of miniaturization. The adoption of automated assembly processes, such as pick-and-place machines, is revolutionizing the field, enabling precision and scalability while minimizing human error. By grasping these fundamental techniques, innovators can push the boundaries of what is achievable in electronic design and manufacturing.
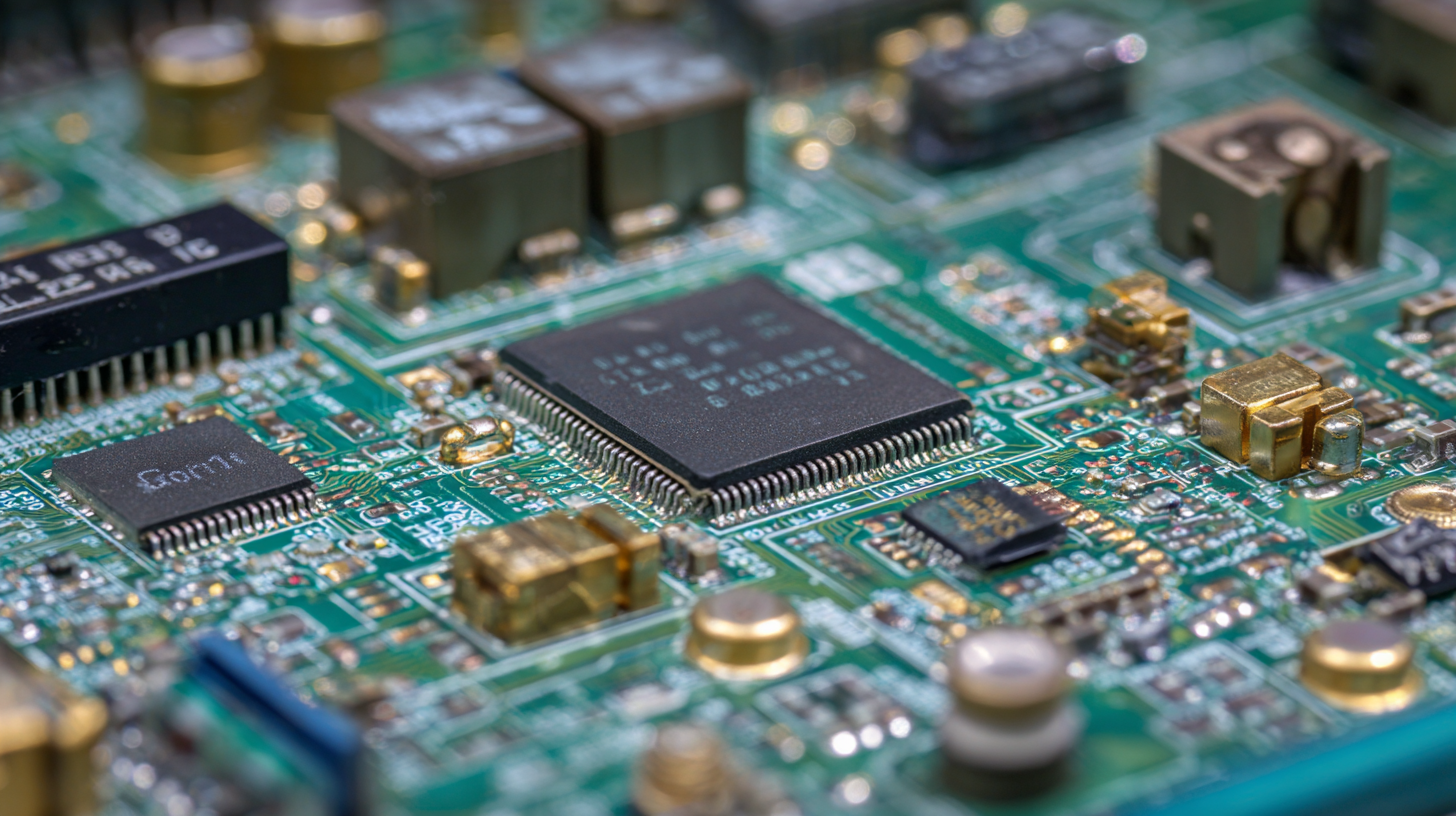
The landscape of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the adoption of innovative materials. Advanced substrates, such as high-frequency laminates and flexible materials, are enabling the production of PCBs that can meet the demands of cutting-edge electronics. These materials not only enhance the performance of electronic devices but also allow for greater design flexibility, paving the way for more compact and efficient products.
Furthermore, the integration of environmentally friendly materials in PCB fabrication is reshaping the industry's approach to sustainability. Biodegradable substrates and lead-free soldering techniques are gaining traction, as manufacturers seek to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining high performance standards. The innovative use of nanomaterials also offers extraordinary properties, such as improved thermal conductivity and electrical performance, which are critical for the advancement of high-performance applications, including 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As these materials continue to evolve, they will redefine the future of PCB manufacturing, fostering new possibilities for innovation in the electronics sector.
The landscape of PCB assembly is rapidly evolving, influenced by emerging technologies that redefine the processes involved. One of the most impactful advancements is the integration of automation and robotics. Automated processes enable faster production cycles and minimize human error, significantly improving efficiency and reliability. Techniques such as robotic pick-and-place systems are now capable of handling a diverse range of components with high precision, paving the way for the mass customization of electronic devices.
Another transformative trend is the adoption of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, in PCB fabrication. This technology not only allows for the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible but also supports the rapid prototyping of PCBs. This agility in design and production is crucial for companies striving to keep pace with the fast-changing demands of the electronics market. Furthermore, the use of smart materials and innovative coatings enhances the performance and longevity of PCBs, making them more suitable for advanced applications such as wearables and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. These emerging technologies are not just reshaping PCB assembly processes; they are laying the foundation for the next generation of innovative electronics.
| Technology | Description | Advantages | Challenges | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing of PCBs enabling complex geometries. | Rapid prototyping, design flexibility, reduced waste. | Material limitations, lower conductivity in some cases. | High potential for custom, low-volume production. |
| Flexible PCBs | Printed circuit boards that can bend and flex. | Space-saving designs, lightweight, and adaptable. | Complex manufacturing processes, potential durability issues. | Growing demand in wearable and portable technology. |
| Automation and AI | Utilization of robotics and AI in assembly lines. | Increased efficiency, consistency, and reduced labor costs. | High initial investment, need for skilled maintenance. | Potential for full automation and smart factories. |
| Embedded Components | Integration of components within the PCB material itself. | Saves space, enhances performance, better thermal management. | Complex design, potential repair difficulties. | Advancements in IoT devices and miniaturization trends. |
| High-Frequency PCBs | PCBs designed for high-speed and high-frequency applications. | Optimized signal integrity, reduced electromagnetic interference. | Higher cost materials, specialized manufacturing requirements. | Critical for telecommunications and advanced computing. |
Sustainability practices in PCB (Printed Circuit Board) fabrication are becoming increasingly critical as the electronics industry seeks to reduce its environmental impact. According to a report from the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits), the global electronics waste is expected to reach 74 million metric tons by 2030, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable manufacturing processes. Implementing eco-friendly materials and waste minimization techniques can significantly lower emissions and energy consumption during PCB production. For instance, using lead-free solder and halogen-free laminates not only improves recyclability but also adheres to environmental regulations.
In addition, advancements in production technology such as additive manufacturing and advanced recycling methods are paving the way for a circular economy within the electronics sector. A recent study from the International Data Corporation (IDC) indicates that companies adopting sustainable PCB practices could improve their operational efficiency by up to 30%. Furthermore, as consumer demand for greener electronics rises, organizations that integrate sustainable practices into their PCB fabrication and assembly will likely gain a competitive edge and enhance their brand reputation. Embracing these sustainability initiatives is not just beneficial for the planet, but it also presents a strategic business opportunity in an evolving market.
The evolution of PCB fabrication and assembly techniques is pivotal for the future of innovative electronics, especially in designing miniaturized medical devices. As devices become smaller, the electrical engineering community faces unique challenges in maintaining functionality without compromising on quality. Best practices include implementing high-density interconnect (HDI) designs, which allow for smaller traces and pads, enabling the integration of more components into a compact layout. According to industry reports, the adoption of HDI technology can increase PCB density by up to 50%, significantly enhancing device performance and reliability.
Tips: Focus on thermal management strategies to prevent overheating in densely packed PCBs. Ensure that your design includes strategically placed thermal vias and pads to dissipate heat effectively. Moreover, consider employing advanced assembly techniques, such as chip-on-board and surface mount technology, to optimize space and improve durability.
In addition, the integration of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs has revolutionized the design landscape, particularly for wearable technologies and conformable electronics. Reports indicate that the flexible circuit market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% by 2025, driven by the demand for innovative solutions in various sectors. Designers should leverage these advancements to reduce weight and enhance ergonomics in their products, ensuring adaptability and comfort for end-users.