In the world of electronics, the circuit board is a fundamental component. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global circuit board market is projected to reach $85.5 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing importance of mastering techniques related to circuit boards. They are essential in various applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices.
Working with circuit boards can be challenging, yet rewarding. Many engineers face issues like faulty solder joints or incorrectly sized components. A report from the IPC shows that 30% of circuit board failures are due to assembly errors. Recognizing this, professionals must pay close attention to detail and continuously improve their skills. Unforeseen mistakes often lead to costly delays, undermining project timelines.
These tips aim to enhance your expertise while working with circuit boards. Learning from past mistakes is crucial. Emphasizing hands-on practice will refine your abilities. As the industry evolves, staying updated on best practices is essential. The journey with circuit boards is filled with challenges and learning opportunities.

Understanding circuit board design and functionality is crucial for anyone working in electronics. A circuit board is the backbone of most electronic devices. It hosts various components that connect to perform specific tasks. Designing a circuit board involves careful planning. Each component's placement affects performance.
Tip: Always start with a clear schematic. It helps visualize connections. Ensure you understand the function of each part. Use proper symbols and notations in your design.
One common mistake is neglecting the layout's impact on signals. Poor placement can lead to interference. For instance, placing power lines too close to signal traces may cause noise.
Tip: Keep traces short and direct for efficiency. Use thicker traces for high-current paths. They reduce heating and voltage drop. Don’t overlook the importance of ground planes. Grounding can affect the stability of a circuit.
Proper spacing between components matters, too. It allows for easier soldering and heat dissipation. Always check for possible collisions between parts during assembly. Circuit boards may seem simple, but they require attention to detail. Each design decision can greatly influence the end product's reliability and functionality.
When working with circuit boards, the right tools make a significant difference. A quality multimeter is essential. It measures voltage, current, and resistance. According to industry data, nearly 75% of electrical failures stem from connections. A good multimeter helps identify these issues quickly.
Soldering irons are another critical tool. A precise temperature-controlled soldering iron can prevent damage to sensitive components. Many professionals suggest keeping tips clean. Dirty tips can lead to poor connections and unsatisfactory results. Industry standards recommend using a soldering iron with a wattage of 25 to 40 watts for most applications.
Moreover, anti-static equipment is vital. ESD wrist straps can save expensive chips from damage. Reports indicate that over 30% of circuit board failures relate to static electricity. Using an anti-static mat can further protect delicate components. Proper organization is also key. Clear containers for small parts can reduce clutter. A well-organized workspace boosts efficiency and reduces frustration. Proper labeling is crucial too. Misplacing a component can waste time. In circuit board work, every detail matters.
When handling circuit boards, safety should always come first. A recent industry report found that approximately 30% of electronics industry workers suffer from injuries related to improper handling. Wearing safety goggles and gloves can prevent many common injuries. Circuit boards can hold static electricity, which may damage components. Use an anti-static wrist strap to minimize this risk.
Tip: Always work in a clean area. Clutter can lead to accidents. Make sure you have enough space to handle tools and components safely.
When it comes to soldering, practice caution with temperature. Soldering irons can reach temperatures of 400 degrees Celsius. This can cause severe burns if mishandled. It’s recommended to use a heat-resistant mat to protect surfaces.
Tip: Allow the soldering iron to cool before putting it down. Improper placement can cause damage. Rushing this process can lead to mistakes. Reflection after each project can help improve techniques. Avoiding complacency is crucial in developing better practices.
Troubleshooting circuit board issues can be tricky. Understanding common techniques will help you fix problems effectively. Start by visually inspecting the board. Look for burnt components or broken connections. A magnifying glass can help reveal tiny cracks. Heat damage often shows dark spots near components.
Multimeters are invaluable for diagnostics. Use them to check voltage and continuity. Testing each component separately may identify the faulty part. A short circuit can disrupt the entire board. Track down unintentional connections between traces. Also, consider reflowing solder joints. This can mend cold solder connections and improve performance.
Documentation is critical in troubleshooting. Keep a log of tests performed and symptoms observed. It helps to have a clear picture of the issue. Sometimes, swapping components can pinpoint the culprit. However, be cautious—this method may lead to further confusion if not done carefully. Remember, it's okay to miss something important during the process; reflection often leads to better understanding.
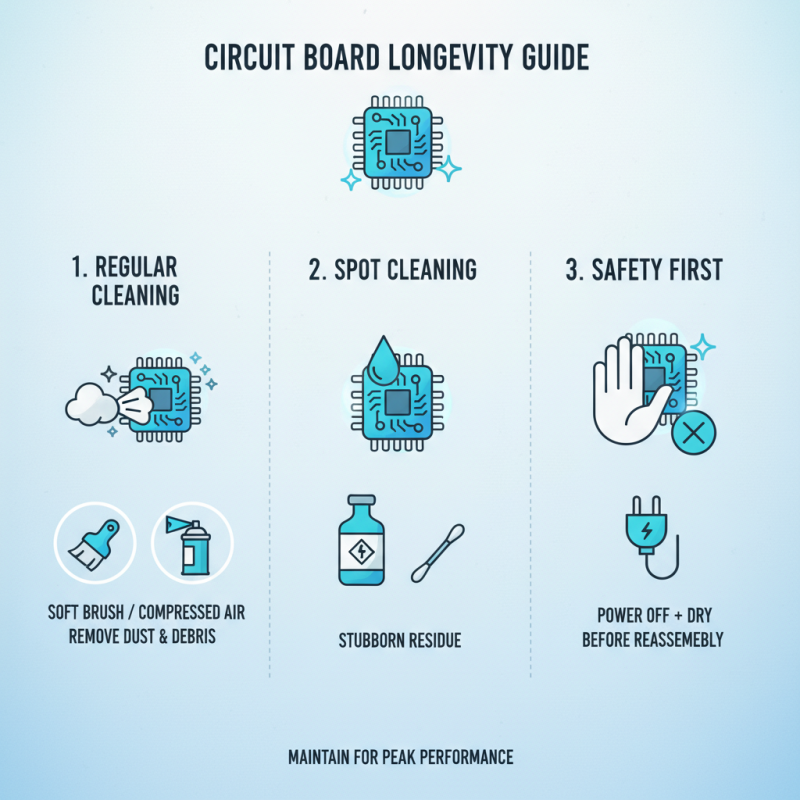
Maintaining circuit boards is crucial for their longevity. Regular cleaning helps prevent dust and debris buildup. Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove loose particles. Isopropyl alcohol works well for stubborn residue. Always ensure the board is powered off and completely dry before reassembly.
Testing circuit boards regularly is equally important. Simple multimeter checks can identify faulty connections. If a circuit is underperforming, inspect solder joints for cracks or the presence of cold solder. Sometimes, the issue might be a worn-out component. Replacing these can enhance performance significantly. Remember that preventive maintenance saves time and money in the long run.
It's easy to overlook minor damage on circuit boards. Visual inspections can reveal issues that testing might miss. Look for discoloration or signs of overheating. Documenting any findings helps track potential recurring problems. Reflection on previous projects can lead to better practices in future work. Be mindful that even small errors can lead to drastic failures.