In the fast-paced world of electronics, the importance of a well-executed PCB assembly prototype cannot be overstated. Engineers across the industry understand that the foundation of a successful electronic device lies in its printed circuit board (PCB). According to Dr. Lisa McCoy, a recognized authority in PCB design and assembly, "The PCB assembly prototype is not just a preliminary step; it is the blueprint for innovation in electronics." Her insights highlight the critical role that prototyping plays in refining product design and ensuring functionality.
As engineers embark on the intricate journey of PCB assembly prototyping, it becomes essential to prioritize precision and accuracy. Each decision made in the prototyping phase can significantly influence the final product's performance, reliability, and manufacturability. From selecting the right materials to adhering to best practices in assembly techniques, understanding the nuances of PCB assembly prototypes can pave the way for groundbreaking developments in electronics.
Embracing the challenges and learning curves associated with PCB assembly prototyping allows engineers to push the boundaries of technology. By focusing on essential tips and strategies, they can enhance their prototyping process, ultimately leading to successful product launches and satisfied end-users. This article aims to equip engineers with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate the intricacies of PCB assembly prototypes, ensuring their projects are built on a solid foundation of expertise and innovation.
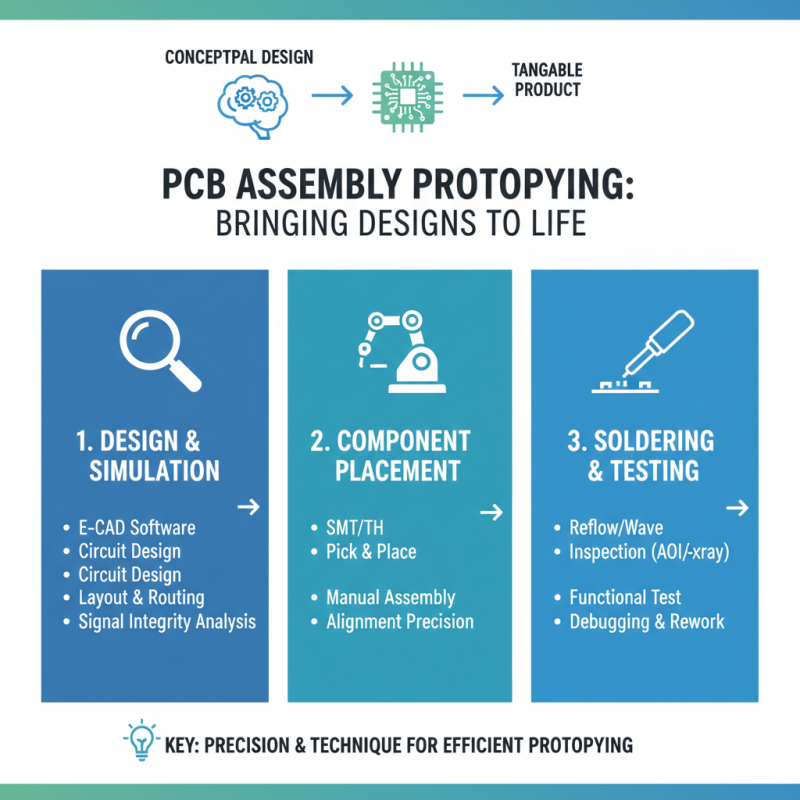
PCB assembly prototyping is a critical phase in the electronics design process, serving as the bridge between the conceptual design and tangible product. Understanding the basics of this process is crucial for engineers who want to bring their ideas to life efficiently. The PCB assembly involves the placement and soldering of electronic components onto the circuit board, which requires a blend of precision and technique.
One essential tip for successful prototyping is to create thorough documentation of your design. This includes schematic diagrams, layout files, and a detailed bill of materials (BOM), which guide the assembly process and prevent costly mistakes. Moreover, utilizing simulation tools before actual assembly can help foresee potential issues, ensuring a smoother transition from prototype to production.
Another important aspect to consider is the choice of components. Opting for widely available and standard components not only simplifies the procurement process but also enhances the reliability of your prototype. Additionally, focusing on a manageable prototype size can lead to quicker iterations. This iterative process is vital as it allows for timely testing and modifications based on performance feedback, helping engineers refine their designs effectively.
When designing effective PCB prototypes, engineers should prioritize several key considerations that directly impact the performance and manufacturability of the final product. First, ensuring the proper component placement is crucial. This involves not only adhering to design rules to prevent overlapping traces but also strategically positioning components to minimize signal interference and optimize heat dissipation.
Additionally, engineers should carefully consider the orientation of components, especially for surface-mounted devices, to streamline the assembly process and reduce the potential for errors.
Another important factor is the selection of materials. The choice of substrate, for instance, can significantly influence the electrical characteristics and thermal performance of the PCB. Engineers should assess factors such as dielectric constant and thermal conductivity to match the material properties with the specific requirements of the project. Furthermore, integrating proper vias and ensuring adequate grounding are essential to maintain signal integrity and minimize noise, particularly in high-frequency applications.
By focusing on these critical design aspects, engineers can create PCB prototypes that are not only functional but also reliable and efficient in real-world applications.
When embarking on PCB assembly prototyping, the right tools and software can significantly streamline the development process, ensuring both efficiency and accuracy. According to industry reports, the global PCB design software market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2022, and it is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9.2%. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on advanced software solutions for PCB design, simulation, and assembly. These tools facilitate intricate designs and allow engineers to visualize and troubleshoot issues early in the design stage, which can save both time and resources.
Essential software includes PCB design tools that offer features such as schematic capture, layout design, and 3D visualization. Additionally, simulation tools that can predict thermal performance and signal integrity issues help to mitigate risks before the physical assembly begins. With the continuous evolution of design software, engineers have access to features like automatic routing and design rule checks, which significantly reduce manual errors and improve overall design efficiency. These advancements are crucial as they enable engineers to meet the increasingly complex demands of modern electronics, where compact designs with high functionality are paramount.
Prototyping printed circuit boards (PCBs) is a crucial step in product development, yet it comes with its own set of challenges that engineers must navigate. One common issue encountered during the PCB prototyping process is design errors. These can arise from an oversight in the schematic or layout phases, leading to functionality issues once the prototype is assembled. To address this, engineers should adopt a rigorous review process, involving simulations and checks at each design stage to ensure that errors are caught early. Implementing design rule checks (DRC) can also significantly reduce the risk of mistakes.
Another significant challenge is component sourcing. With the rapid pace of technology advancement and the frequent introduction of new components, it can be difficult to find the right parts in time for prototyping. This challenge can be mitigated by maintaining good relationships with multiple suppliers and staying updated on component availability. Additionally, engineers should consider designing prototypes with alternative components in mind, allowing for flexibility in sourcing. By anticipating sourcing issues and adapting designs, engineers can streamline the prototyping process and minimize delays.
When it comes to testing and validating PCB prototypes, engineers should prioritize a systematic approach to ensure reliability and functionality. One of the most crucial practices is to conduct thorough electrical testing. This involves checking for continuity, shorts, and component improper placement. Using automated testing equipment can streamline this process, enabling engineers to quickly identify issues that could hinder the performance of the final product.
In addition to electrical testing, thermal analysis is essential in validating PCB prototypes. Engineers should monitor the heat distribution across the board and evaluate the thermal management strategies used. Techniques like thermal imaging can help identify hot spots and potential failure points. Furthermore, implementing environmental testing, such as humidity and vibration tests, can assess the durability of a PCB under various conditions, ensuring that it meets long-term operational criteria. By adhering to these best practices, engineers can significantly enhance the reliability of their PCB prototypes, paving the way for successful product development.