The realm of electronic circuit boards (ECBs) has become increasingly pivotal in our technologically-driven world. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the global electronic circuit board market is anticipated to reach $83.9 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2021. This growth emphasizes the importance of understanding the fundamental principles and design techniques required for creating effective and functional circuit boards.
As we delve into the intricacies of designing an electronic circuit board, it is essential to grasp the essentials that govern this intricate process. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Zhang, a leader in PCB technology, asserts, "A well-designed electronic circuit board is the backbone of any electronic device, impacting performance and reliability." This sentiment captures the essence of why mastering the design of electronic circuit boards is crucial for anyone looking to venture into the electronics field, whether as a hobbyist or a budding engineer.
In this guide, we will explore the fundamental concepts and practical steps necessary to design an electronic circuit board, equipping beginners with the tools to innovate and create. Understanding the dynamics of circuit board design not only enhances individual projects but also contributes to the broader technological landscape, fostering innovation and efficiency in electronic devices all around us.

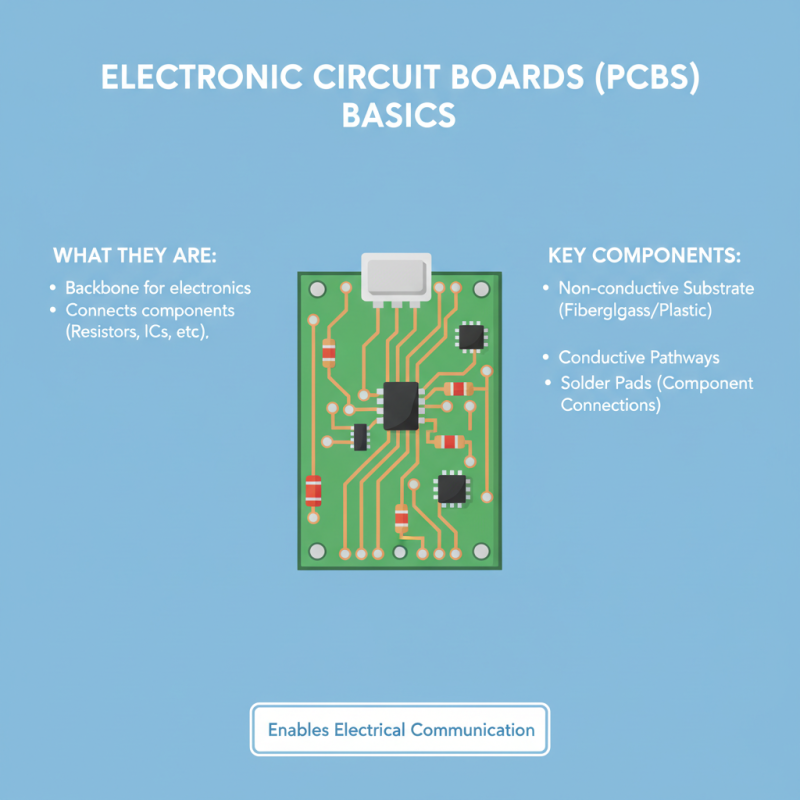
Understanding the basics of electronic circuit boards (PCBs) is essential for anyone interested in electronics. At their core, circuit boards serve as the backbone for electronic devices, providing a platform for connecting various components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. A typical PCB is composed of a non-conductive substrate, usually made of fiberglass or plastic, over which conductive pathways are etched or printed. These pathways allow for the flow of electrical current, enabling communication between components.
When designing a PCB, it is crucial to begin with a schematic diagram that outlines the connections and functions of each component. This diagram acts as a blueprint for the layout of the PCB. Once the schematic is finalized, the physical arrangement of components must be considered to optimize space and functionality. Factors such as trace width, spacing, and component placement are vital to ensure efficient signal integrity and minimize interference. Additionally, beginners should familiarize themselves with tools like PCB design software, which simplifies the creation of intricate designs and allows for easy modifications.
Overall, grasping the fundamentals of electronic circuit boards paves the way for budding engineers and hobbyists to dive deeper into the world of electronics. With practice and patience, anyone can develop their skills in designing effective and reliable PCBs, transforming their ideas into functional electronic devices.
When embarking on the journey of circuit board design, having the right tools and materials is crucial for beginners. According to a recent industry report from the PCB Design Community, approximately 45% of novice designers encounter delays and failures in their projects due to inadequacies in their tool selection and material quality. To streamline the design process, understanding the essential tools such as schematic capture software, PCB layout software, and simulation tools is vital. Programs like these allow designers to visualize their circuits, troubleshoot potential issues, and ensure a robust layout before manufacturing.
In addition to software, the choice of materials cannot be overlooked. The substrate, usually made from fiberglass or resin, should be selected based on the intended application of the circuit board. A report by the International Electronics Manufacturing Initiative (iEmi) indicates that the right substrate can improve durability and thermal performance, significantly impacting the efficiency of electronic devices. Knowledge of components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, is also essential. Utilizing reliable sources for components can enhance your design's performance, and industry surveys show that over 60% of successful projects stem from informed material choices. By focusing on these foundational tools and materials, beginners can significantly improve their chances of creating effective and reliable circuit boards.
Designing an electronic circuit board can initially seem overwhelming for beginners, but breaking it down into manageable steps can simplify the process. The first phase involves creating a schematic design, which serves as the blueprint for your circuit. Begin by determining the components you will use, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. Use a schematic drawing tool to place these components on the canvas. Remember to connect them using lines that represent electrical paths. Every connection should be clear and logical to avoid confusion in later stages.
Tips: When working on your schematic, keep your layout organized. Group related components together to enhance readability. Additionally, label each part clearly to ensure that anyone reviewing your schematic can easily understand its function. It may also help to use color coding for different types of connections, which can make the circuit easier to follow.
Once your schematic is complete, the next step is to verify its functionality. This means checking if all connections are made correctly and if the component specifications meet the circuit requirements. Simulation software can be valuable here, as it can test your design without the need for physical components.
Tips: Before finalizing your design, always double-check your work for errors. Look out for common mistakes, such as unconnected pins or incorrect polarity. Engaging with online communities can also provide valuable feedback and insights from more experienced designers, helping you refine your schematic even further.
When designing an electronic circuit board (PCB), the layout and routing of circuit components are crucial elements that significantly impact both the functionality and manufacturability of the final product. Proper layout techniques can enhance signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), an essential consideration given that studies have shown that up to 30% of circuit failures in designs are related to poor layout practices. Beginners should prioritize creating a schematic diagram that accurately represents the intended circuit, ensuring connections are well-defined before commencing the physical layout.
Routing involves placing traces that connect different components. It is vital to adhere to specific design rules, such as maintaining adequate trace width to handle current loads, which is typically dictated by IPC-2221 standards. For instance, a trace carrying 1A of current should be approximately 0.5mm wide when using 1oz of copper, according to industry reports. Furthermore, it's advised to keep power and ground planes separate from signal traces to minimize noise. Research indicates that effective routing strategies, which include using shorter and wider traces, can yield a reduction in unwanted resistive effects by up to 20%, ultimately leading to a more reliable and efficient PCB design for electronic devices.
Testing and troubleshooting an electronic circuit board (PCB) is an essential skill for beginners looking to deepen their understanding of electronics. The PCB serves as the backbone of most electronic devices, and ensuring its functionality through rigorous testing can save time and resources in the long run. According to a report from the IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries), improper testing during the design phase can lead to a 50% increase in development costs, highlighting the importance of systematic testing methods.
One effective approach in troubleshooting circuit boards involves using a multimeter to check for continuity, voltage, and resistance. This tool allows users to identify faulty connections or components quickly. In fact, research by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) found that 70% of all PCB issues stem from poor connections or soldering defects. Regular testing at various stages of the assembly process can help catch these issues early. Whether it's verifying solder joints or checking component placements, a diligent testing strategy can significantly enhance the reliability of the finished product.
Additionally, software tools equipped with simulation capabilities can be utilized to test circuits before physical assembly. This not only reduces the likelihood of errors but also helps in understanding how the circuit behaves under various conditions. The use of such simulation tools has been shown to reduce development time by up to 30%, according to findings from the Journal of Electronic Testing. By integrating comprehensive testing and troubleshooting practices, beginners can build robust circuit boards that function correctly and efficiently, fostering a cycle of continuous improvement and learning.